
CultivAcing Knowledge:
Exploring the Fascinating World of Agriculture

Why Liquid Micronutrient Fertilizer Matters—And What Indiana Corn Just Proved About ZnAce
When a grower in Indiana saw a 245% zinc uptake using ZnAce, it proved just how effective liquid micronutrient fertilizers can be. Here’s why it worked—and what it means for your next foliar pass.

Liquid Micronutrient Fertilizer Foliar Sprays: The Underrated MVP in Corn and Soybean Yield
Liquid micronutrient fertilizer foliar sprays are the overlooked MVPs in yield optimization. See how acetate-based formulas drive crop performance and nutrient efficiency.

Free Phos 24: Liquid Phosphate Fertilizer That Outperforms in California Trials
In California trials, Free Phos 24 delivered 8% higher yields and better ROI than standard 9-24-3 liquid phosphate fertilizer—using 40% less product. Learn how this enhanced-efficiency solution is helping growers do more with less.
Nutrient Efficiency: The Dual Benefits of CultivAce Acetates and Free Phos 24
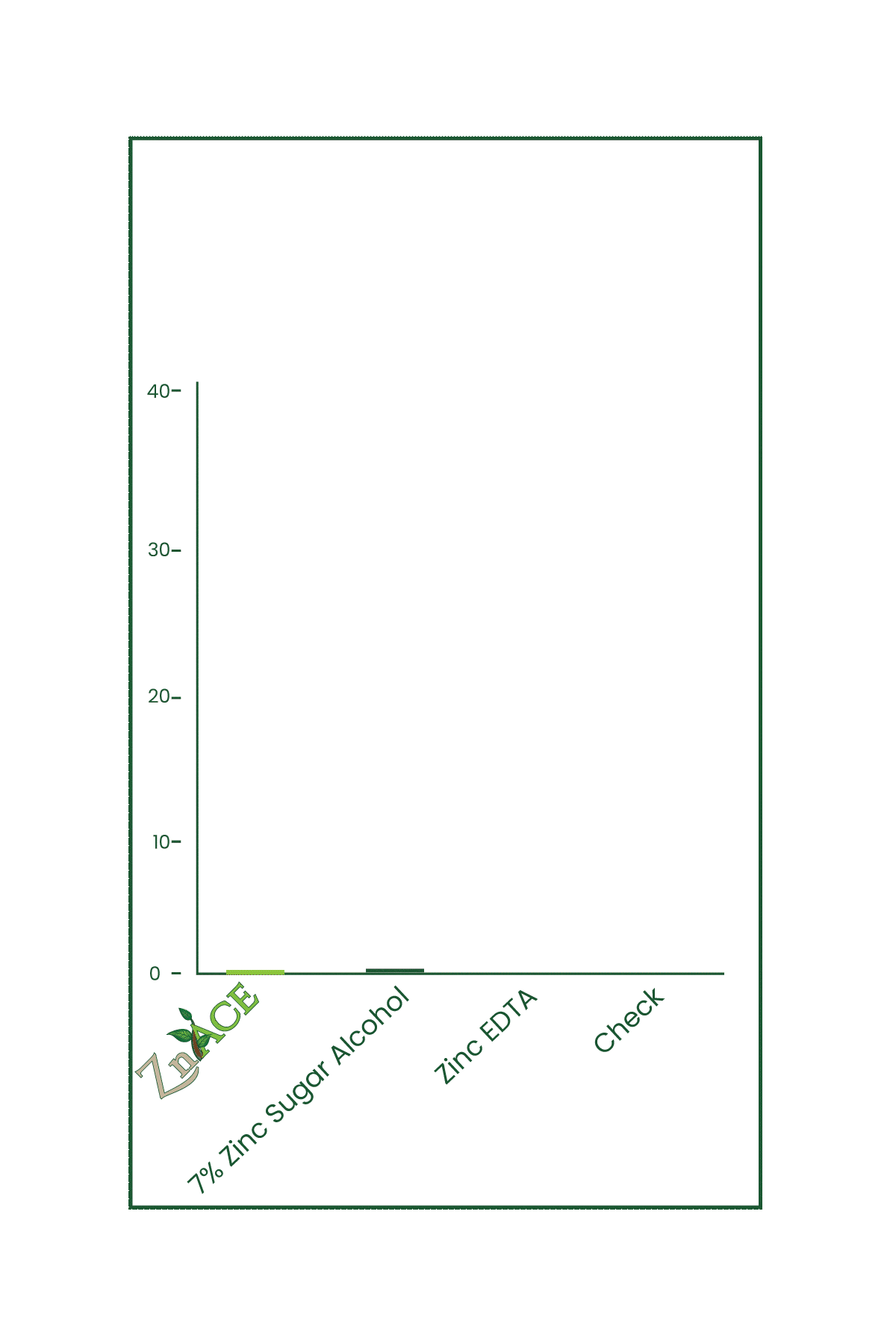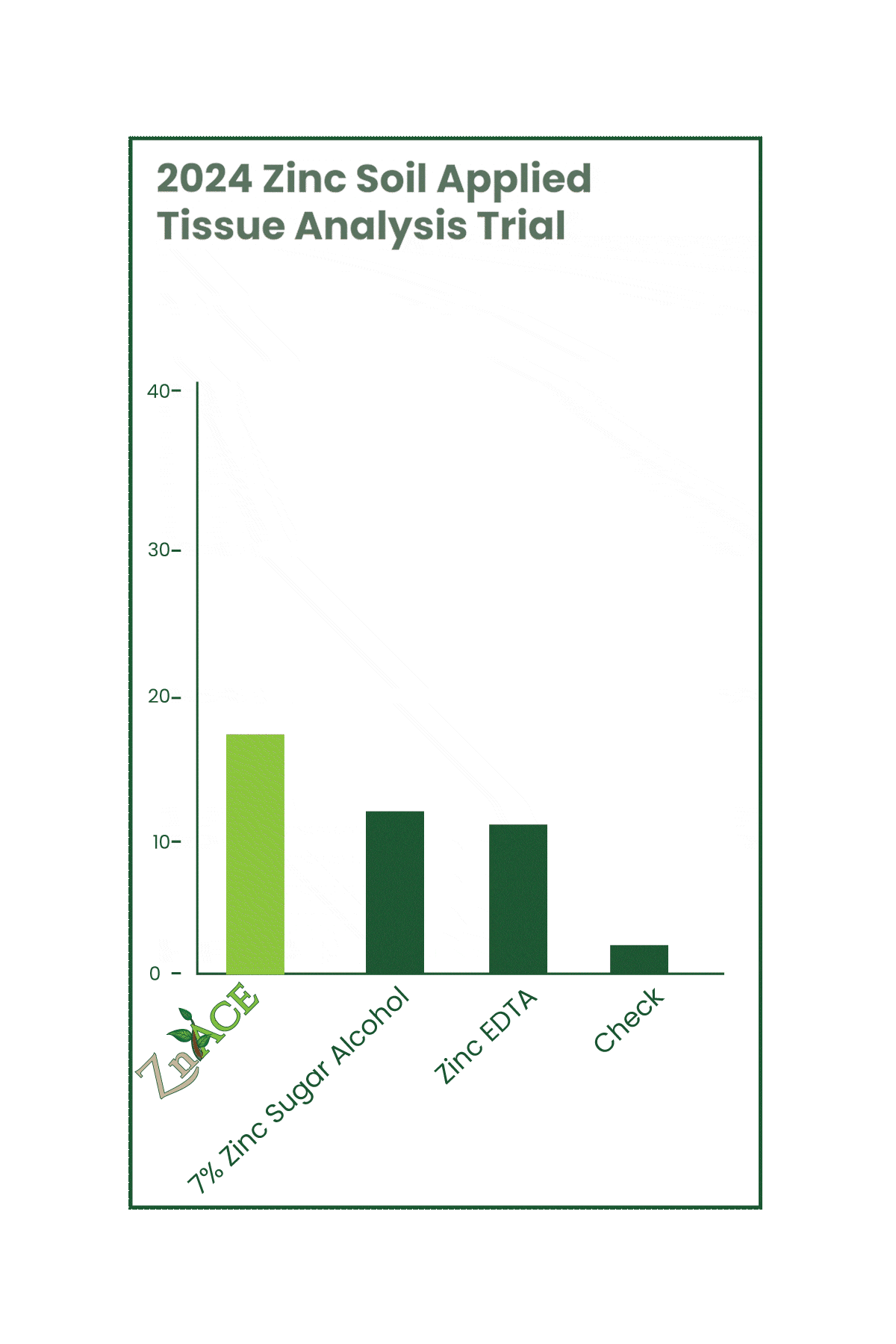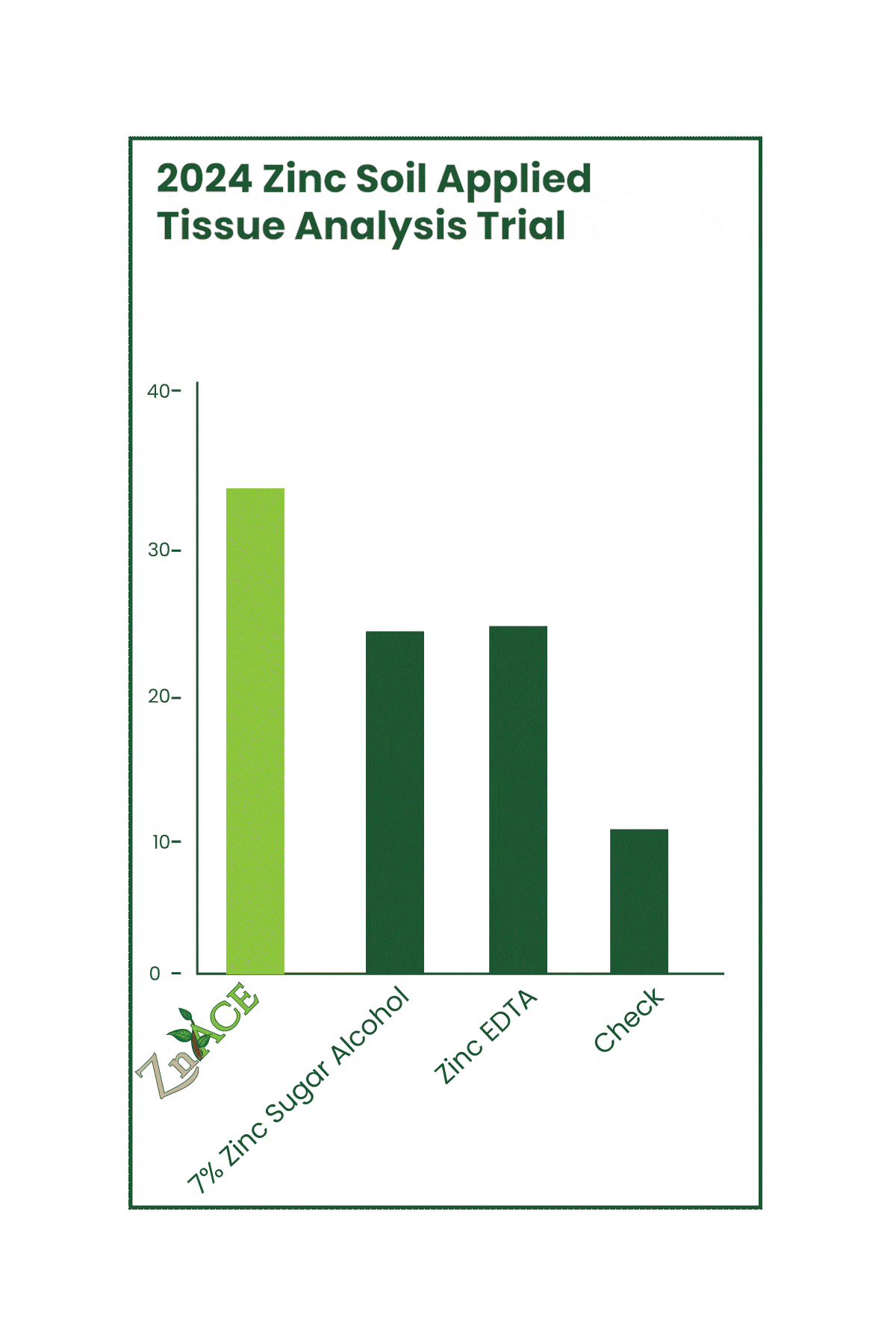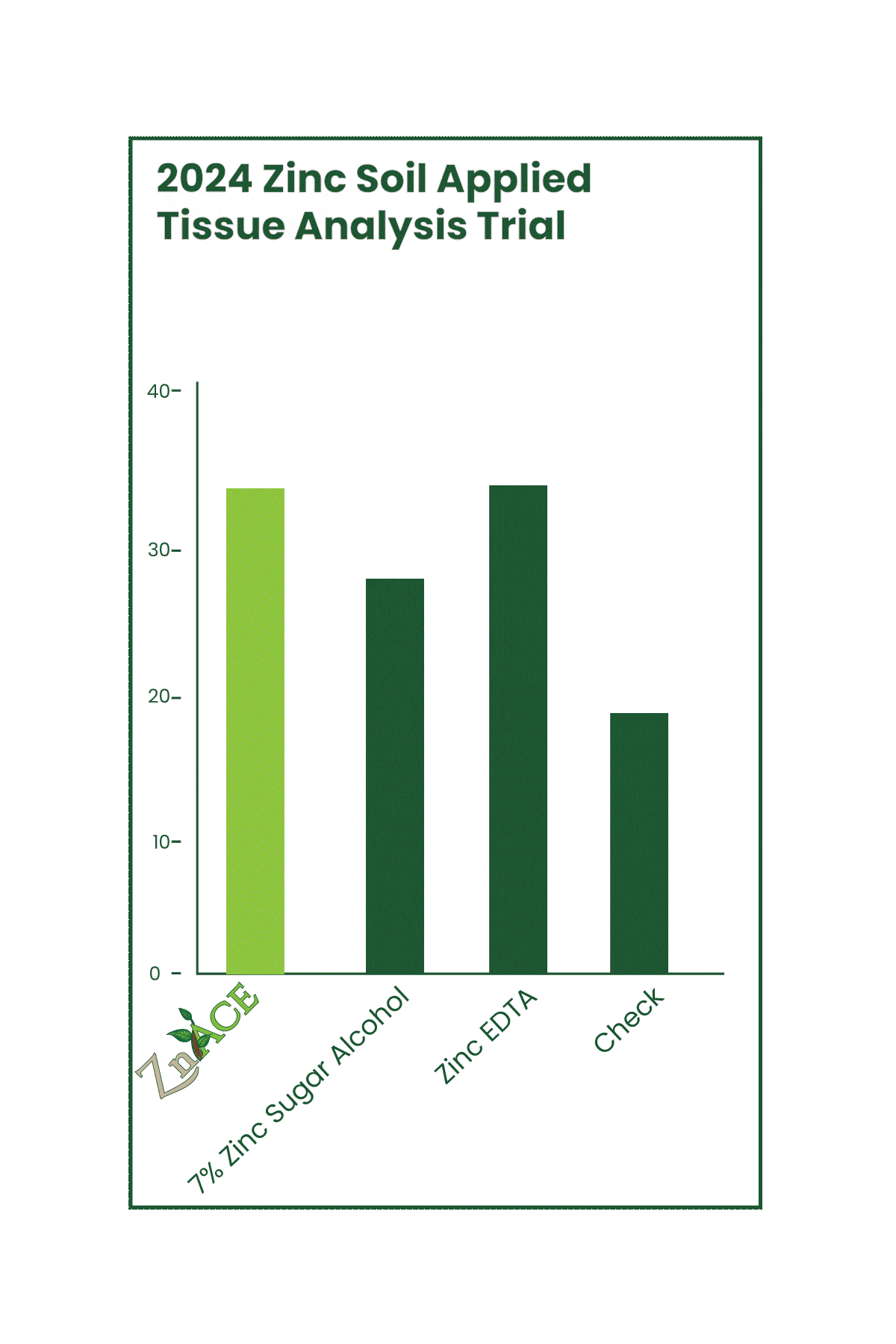
CultivAce acetate fertilizers aren’t just for foliar applications—they’re proving to be just as effective in soil applications. Recent trials showed that our ZnAce (8% zinc acetate) outperformed both zinc sugar alcohol and Zinc EDTA in increasing tissue zinc concentration by up to 100%. This supports the dual benefit of CultivAce acetates, working effectively in both the soil and on the foliage.
In a separate trial, our Free Phos 24 liquid phosphate fertilizer, applied at just 3 gallons per acre, demonstrated a significant boost in yields—up to 14 bushels more than the grower’s standard. With reduced input, less fuel, and more acres covered, Free Phos 24 proves that efficiency and high yield aren’t mutually exclusive.
By encouraging microbial processes like phosphate mineralization and solubilization, Free Phos 24 allows plants to access more phosphorus from the soil, reducing the need for excessive nutrient applications and increasing sustainability.

Monsters in Minnesota: Liquid Phosphate and Acetate Foliar Fertilizer Affects
Minnesota’s sugar beets have seen a surprising boost this season, with liquid phosphate and acetate foliar fertilizers making a noticeable difference. Recent trials highlight the contrast between untreated crops and those benefiting from Free Phos 24, showing how these fertilizers can quietly, but significantly, improve both yield and sugar content. Here's what the latest results are showing.

8 Micronutrient Foliar Sprays: What Growers Should Know
Understanding the role of micronutrient foliar sprays is crucial for optimizing crop health and yield. While Clemson University identifies seven essential micronutrients—boron, zinc, manganese, iron, copper, molybdenum, and chlorine—Ohio State University adds an eighth, nickel, to the list. But not all of these are equally vital for every crop or situation. Timing and nutrient availability are just as important as the micronutrients themselves. By referencing tools like Mulder’s Chart, growers can navigate the complex interactions between nutrients and make informed decisions about their micronutrient foliar spray applications. This strategic approach can help prevent deficiencies and enhance crop performance.

On the Ground: Liquid Phosphate Fertilizer's Impact on Minnesota Crops
Our recent trip to Minnesota's fields revealed remarkable results with Free Phos 24 liquid phosphate fertilizer. Despite challenging weather, our sugar beet and corn plots showed significant improvements in root biomass and overall plant health.
Curious about how liquid phosphate fertilizer can enhance your crop yields? Join us on this journey towards better crop production and see the benefits firsthand!

2024: Impact of Liquid Phosphate Fertilizers in No-Till Farming
Discover how Free Phos 24 liquid phosphate fertilizer is revolutionizing corn farming! Our latest field trials in Wisconsin and Kansas show remarkable results with stronger roots and higher yields. Dive into the details and see why farmers are choosing Free Phos 24.

EDTAs vs. Acetates: Maximizing Foliar Nutrient Spray Absorption for Higher Yields
Are you relying on EDTA-chelated nutrients for your foliar sprays? While these products are commonly used to enhance plant growth, crop quality, and disease resistance, recent research indicates they might be doing more harm than good. In this blog post, we delve into university and third-party studies to explore the impact of EDTA-chelated nutrients on foliar applications and compare them with acetates. Discover the critical differences and how they can influence your crop's health and your bottom line.


The Future of Crop Production: Exploring the Impact of Biologicals and Biostimulants at the No-Till Conference
Discover the latest trends in sustainable agriculture with a focus on biologicals and biostimulants, as revealed at the No-Till Conference.

Comparing Liquid Phosphate Fertilizers: Midwest Corn Yields
Local Midwest growers are uncovering the untapped potential of this innovative liquid phosphate fertilizer. Preliminary results from Kansas are in, revealing not just improved yields but also remarkable cost-efficiency. Join us as we unveil these exciting developments, marking a significant stride in sustainable agriculture and efficient fertilization.

Orthophosphate vs. Polyphosphate: Understanding the Differences
Discover the crucial distinctions between orthophosphates and polyphosphate fertilizers in our detailed blog. Gain insights into their effects on crop growth and yield. Dive into the comparison of Orthophosphates vs. Polyphosphate Fertilizers now.

An Interview with Dr. Dan Quinn of Purdue University
Dr. Dan Quinn grew up in central Michigan in a small town between Grand Rapids and Lansing and has been surrounded by Ag his whole life. This led him to two degrees at Michigan State university.

An Interview with Dr. Khan and Dr. Mulvaney – Authors of the Potassium Paradox
Having read the paper, "The Potassium Paradox" myself, I thought that it would be interesting to track down the researchers at the University of Illinois who wrote the paper and ask them a few questions I had about their research.

Are You Wasting Precious Profit on Plant Nutrients?
It is commonplace in many parts of the US to fall-apply phosphorus and potassium. Growers often think this practice can build soil P and K levels while increasing yield and maintaining soil nutrient availability.

Applying Phosphorus and Potassium - New Research
It is commonplace in many parts of the US to fall-apply phosphorus and potassium. Growers often think this practice can build soil P and K levels while increasing yield and maintaining soil nutrient availability.

Calcium – How Much Does the Soil Need?
How much calcium do we need in our soil? If you use a Morgan test, you should have a minimum of 2,000# per acre and as a percent of base saturation…

FREE pHOS 24
Why did we name this product FREE pHOS 24? Soil applied phosphate is terribly inefficient. Only about 5% to 10% of what is applied to the soil is available for use by the plant.
Less Applied and More Phosphate in the Plant
In early March of this year, the grower applied 10 gallons per acre of EVEN MORE 8-24-0 on pistachios thru drip irrigation. In prior years, they were applying a competitor 7-21-0 at 15 gallons per acre.
