No Till Farmer - Acetates vs EDTAs
Webinar with Wayne Sledge
Earn (.5 credit hours) for Certified Crop Advisor from the American Society of Agronomy
2023 & 2024 Plant Tissue Trial Results
THE PROOF IS IN THE NUMBERS
Advantages of Acetates
for Nutrient Delivery
Small molecules are easily absorbed and plants accept the carrier as a native substance.
Larger compounds can prevent absorption and the plant may reject the foreign carrier.
Iron Acetate Molecular Size
173.93 g/mol
EDTA Molecular Size
435 g/mol
Effect of EDTA on the Foliar
Absorption of Trace Element Fertilizers
-Samuel P. Stacey & Derrick M. Oosterhuis - University of Arkansas Researchers
EDTA significantly reduces the absorption of Fe and Zn in foliar fertilizers, making it less effective and more costly for farmers. EDTA's high molecular weight and negative charge hinder nutrient uptake through leaf cuticles.
5% Mn Acetate
vs. 5% EDTA &
Amino Acid Chelate
29.28% increase in tissue analysis.
In 2024, each product was applied at 2 quarts per ace. MnAce increased tissue manganese levels by almost 30% over the amino acid chelate.
5% Iron Acetate
vs. 3% Iron EDDHA
53.89% increase in tissue analysis.
In 2024, each product was applied at 2 quarts per ace. FeAce increased tissue iron levels by 31.5 ppm over the EDDHA.
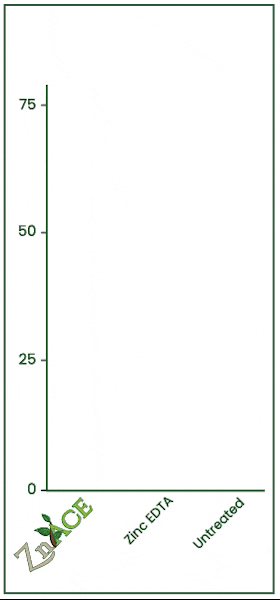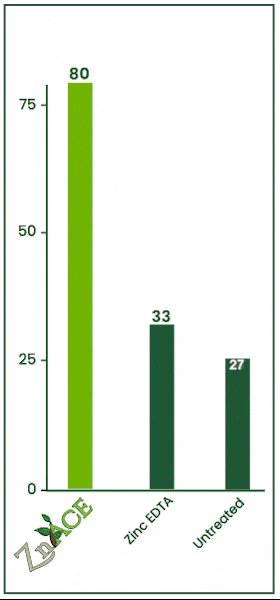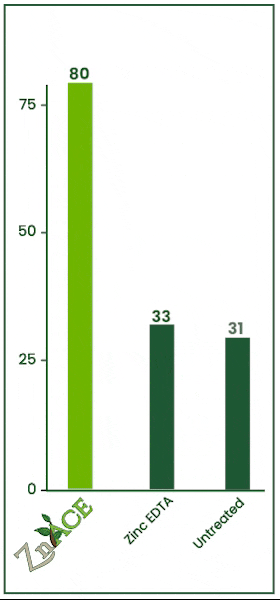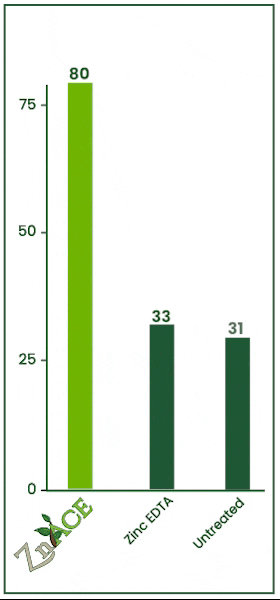
8% Zinc Acetate
vs. Zinc EDTA
47 ppm increase in tissue analysis.
In 2023, each product was applied at 2 quarts per acre. ZnAce increased tissue levels by 47 ppm over EDTA.
8% Zinc Acetate
Soil Applied Trial
22.87% increase in tissue analysis.
Zinc Acetate, Brandt Manni-Plex Zinc, and Zinc EDTA were tested via drip irrigation. Zinc Acetate was applied at 64 fl oz/acre. Tissue zinc concentrations were measured 6 days after application as seen in the graph on the left.
Zinc Acetate outperformed Manni-Plex, increasing zinc levels by 22.87% and by 100% over the untreated check. Zinc Acetate and Zinc EDTA performed similarly, proving Zinc Acetate is effective for both foliar and soil applications.
ZnAce is a versatile, dual-threat product for both foliar and soil application, consistently outperforming competitors and significantly increasing zinc concentrations in plants.
8% Zinc Acetate
vs. Zinc EDTA
47 ppm increase in tissue analysis.
In 2023, each product was applied at 2 quarts per acre. ZnAce increased tissue levels by 47 ppm over EDTA.
8% Zinc Acetate
Soil Applied Trial
22.87% increase in tissue analysis.
Zinc Acetate, Brandt Manni-Plex Zinc, and Zinc EDTA were tested via drip irrigation. Zinc Acetate was applied at 64 fl oz/acre. Tissue zinc concentrations were measured 6 days after application as seen in the graph on the left.
Zinc Acetate outperformed Manni-Plex, increasing zinc levels by 22.87% and by 100% over the untreated check. Zinc Acetate and Zinc EDTA performed similarly, proving Zinc Acetate is effective for both foliar and soil applications.
ZnAce is a versatile, dual-threat product for both foliar and soil application, consistently outperforming competitors and significantly increasing zinc concentrations in plants.
Review our full range of acetate fertilizers, formulated to provide essential nutrients for your crop. With eleven high quality products available, we aim to support optimal growth and productivity for America’s growers.